The manifestation of psoriasis on the face is a rare and atypical phenomenon. Its main danger lies not on the physiological level, but on the psychological one. A person faced with such a course of the disease often withdraws, experiences communication difficulties and runs the risk of falling into severe depression. Meanwhile, the problem can be solved by achieving long-term stable remission. The main thing is to consult a specialist in time and not to self-medicate.
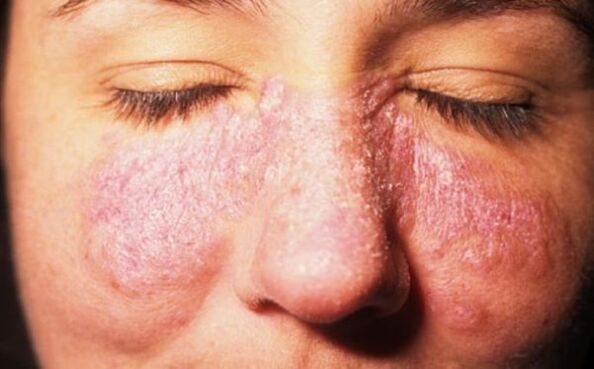
What is psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic disease of a non-infectious nature, accompanied by very unpleasant symptoms, including reddish rashes and peeling of damaged areas of the skin.
They arise due to a disruption of the replacement mechanism of the dermis layer. In a healthy person, this process lasts on average 30 days; in a sick person, the skin renews itself in less than a week. The body perceives such a rapid formation of new cells as an aggressive invasion and gives an immune response, "sending" an increased number of leukocytes and red blood cells to the site of probable damage, provoking inflammation.
Most often, rashes characteristic of the disease form on the elbows and knees, in the armpits and on the head under the hair. In rare cases, manifestations of the pathology spread to the face. Scientists are still understanding the causes and mechanisms of the disease.
Causes of psoriasis and risk factors
The nature of psoriasis has been discussed in the scientific community for several decades. Three theories on the onset of the disease are the most widespread:
- autoimmune;
- endocrine;
- psychosomatic.
In recent years, the genetic explanation for the appearance of psoriasis has gained popularity. This is confirmed by statistical data, according to which the majority of patients have close relatives suffering from this disease.
Supporters of various theories agree on three points:
- the polyetiological nature of psoriasis, that is, the origin of the pathology is caused by different reasons;
- the disease is not contagious;
- stable remission can be achieved.
Doctors have also identified the main factors that provoke the disease. Between them:
- chronic inflammation;
- severe traumatic skin damage;
- metabolic disorders;
- severe poisoning;
- weak immunity;
- constant stress;
- freezing;
- infectious diseases;
- alcoholism;
- certain medications (such as beta-blockers and antibiotics).
People whose bodies are affected by more than two factors from the list above are at greatest risk. There is a possibility that they will encounter the most unpleasant and atypical form of the disease.
The mechanism of appearance of psoriasis on the face
Facial psoriasis is characterized by rapid development due to particularly sensitive skin. It manifests itself in different ways, but doctors distinguish three general phases:
- progressive;
- stationary;
- regressing.
In the last stage, the psoriatic manifestations fade and disappear completely. The whole process, depending on the severity and type of disease, lasts from two months to six months.
The classification of psoriasis is complex and involves many varieties. According to the type of progression, two large groups are conventionally distinguished: pustular (with rashes in the form of purulent pustules) and non-pustular. Depending on the severity, area of damage and intensity of manifestations, psoriasis can be mild and severe. The severe form of psoriasis characteristic of the face, seborrheic, does not fall into the general classification.
Attention! A dangerous complication of this form of the disease is infection of the sebaceous glands by fungi.
The symptoms of psoriasis subtypes are clearly visible, which allows the competent doctor to accurately diagnose the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
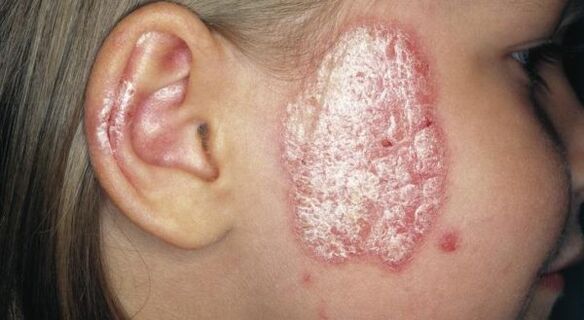
Symptoms of psoriasis on the face
Signs of the early stage of the disease can easily be confused with symptoms of an allergy or irritation. In addition, they appear on the face during the periods of maximum vulnerability of the skin - in the autumn-winter period. Psoriasis can be suspected based on the following symptoms:
- skin redness;
- the appearance of dandruff;
- itching;
- small wounds;
- peeling;
- formation of yellowish crusts.
The first spots are no larger than the head of a pin and appear on the forehead and cheeks. Then they grow and, fusing together, turn into red papules that cause a lot of itching.
Attention! Scratching the rashes accelerates the spread of the papules, which can leave scars.
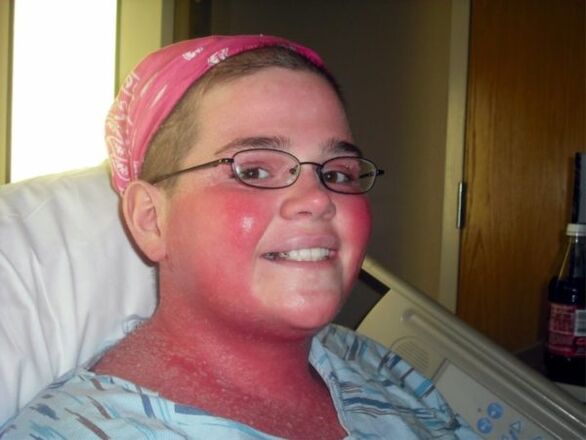
Gradually, the papules cover larger and larger areas of the skin and form on the lips, nose, ears, and scalp. The plaques begin to bleed when pressed; the scales stick together due to the secretion of the sebaceous glands, forming a dense yellow crust. The epidermis thins and loses its ability to perform protective functions from external influences. It is better to start treatment at an early stage of the disease. Only a dermatologist can determine the degree and type of disease.
Differential diagnosis
Establishing the correct diagnosis is not difficult for a competent specialist. It is based on data on symptoms and the course of the disease, as well as on visual examination. The so-called psoriatic triad, which is discovered during the process of scraping the problem area of the skin, has great diagnostic value. It includes three phenomena:
- stearin stain (increased flaking after scraping);
- terminal pellicle - a smooth surface in place of the removed scales;
- blood dew: the appearance of droplets of blood.
Psoriasis sometimes looks similar to other diseases. Differential diagnosis is often carried out with pathologies such as:
- syphilis;
- some varieties of lichens;
- pityriasis;
- chronic dermatitis;
- eczema;
- parapsoriasis.
To clarify the diagnosis in controversial cases, the following are prescribed:
- allergy tests;
- blood test for biochemistry;
- histological examination of the skin;
- UAC;
- stool examination for dysbacteriosis;
- Ultrasound;
- x-ray (to rule out psoriatic arthritis).
Unfortunately, having discovered the first signs of psoriasis on the face, many patients begin to self-medicate, which only worsens the situation. Meanwhile, modern medicine offers sufficient tools and techniques with which it is possible to forget about an unpleasant disease for a long time.

Treatment tactics
To successfully eliminate psoriasis requires an integrated approach and strict adherence to medical recommendations. Treatment methods typically used include:
- pharmacological therapy;
- local impact;
- phototherapy;
- Physiotherapy;
- folk remedies.
It is also important to follow a special diet.
Pharmacological treatment
Drugs are prescribed for the treatment of seborrheic psoriasis on the face in advanced form. Usually the following groups of drugs are used:
- antimicrobials help reduce the intensity of psoriatic manifestations;
- a drug with succinic acid normalizes cellular immunity and increases the flow of oxygen to tissues;
- antihistamines reduce itching and swelling;
- glucocorticosteroids;
- sedatives are included in the complex treatment for stress relief. You can take valerian or motherwort extracts;
- Folic acid helps normalize pigmentation and purify the skin.
Attention! Any medications must be taken strictly as prescribed by your doctor.
If the use of these drugs does not bring a positive result, use Cyclosporine. It is prescribed in severe cases due to the large number of side effects.
Local agents
Ointments, creams and gels in the treatment of psoriasis help relieve inflammation, soften plaques, help reduce itching and disinfect damaged facial skin. The most effective remedies include ointments:
- Salicylic;
- naphthalene;
- Sulfur tar.
In extremely severe cases, a dermatologist may recommend topical hormonal medications. They have a number of contraindications, so it is strictly prohibited to use them independently.
Attention! It is not possible to mask psoriatic plaques with a cosmetic foundation! It will clog pores and block oxygen access to damaged tissue.
The effect of medicinal ointments is enhanced by the use of moisturizing and soothing preparations with shark oil or vitamin F. Physiotherapy will speed up the healing process.
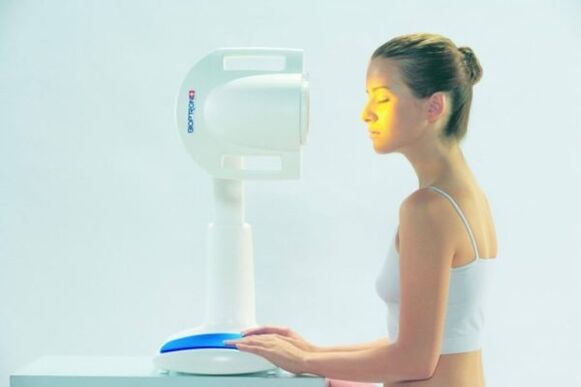
Physiotherapy
In most cases, patients suffering from psoriasis will have to undergo a course of phototherapy: this method restores the ability of the tissues to regenerate by exposing the facial skin to ultraviolet light and stimulating the production of vitamin D. Depending on the symptoms and features of the course of the disease, hardware manipulations such as:
- X-ray therapy;
- Ural Federal District;
- electrosleep;
- laser exposure;
- ultrasound;
- magnetotherapy.
These procedures directly affect the foci of inflammation, contribute to their localization and elimination. Improves the patient's general condition, including the psychological one. Recipes of traditional medicine will be a good addition to conservative treatment.
Folk remedies
Homemade remedies based on herbs and medicinal plants will help relieve the most unpleasant symptoms of the acute period of psoriasis. Here are some popular recipes:
- Prepare a spoonful of chamomile flowers with 200 g of hot water and let it brew (about an hour). In the cooled and filtered solution, generously moisten a cotton cloth and apply it to the face for 30 minutes;
- combine solid oil and birch sap in equal proportions. Apply the resulting mass evenly to the affected areas and leave for 20 minutes. Wash and lubricate your face with a moisturizer;
- Place a few aloe leaves in the refrigerator for a week, then remove them, chop them up and apply them to your face for 30 minutes.
Very useful for psoriasis are products based on essential oils and sea salt washes. In addition to taking care of your face, a correct and balanced diet plays an important role in eliminating psoriasis.

Diet
Nutrition for psoriasis should include all the substances necessary for the body. It is especially important to eat more fiber. The diet must include sufficient amounts of fruits, vegetables and dairy products. You can't eat:
- sweet baked goods;
- chocolate;
- milk with a high percentage of fat;
- peanuts;
- any citrus fruits;
- spices and aromatic herbs;
- alcoholic beverages.
Dishes should not be fatty, fried, smoked or excessively spicy. Once a week it is worth organizing fasting days "on kefir".
Prevention
People predisposed to psoriasis must take simple precautions:
- wash with special products with a moisturizing effect;
- Clean your face daily with decoctions based on chamomile or hops, especially when it is hot or freezing;
- stop smoking;
- avoid prolonged stay in dusty or humid environments;
- spend more time in the sun.
Visit your dermatologist regularly to prevent the condition from worsening. It is impossible to completely cure psoriasis. However, by observing preventive measures and following medical recommendations, it is possible to achieve stable remission and lead a satisfying lifestyle.
























